When it comes to Latin America on the other side of the ocean (hereinafter referred to as Latin America), many people's first impressions are football, rainforest, carnival, or the magical and bizarre world in Marquez's One Hundred Years of Solitude. With the development of cross-border trade system under economic globalization, this magical land gradually faded from the mysterious veil in the eyes of sellers in China.
Latin America generally refers to the American region south of the United States, including Mexico, Central America, West Indies and South America in North America. Because this region has long been a colony of Latin-speaking Spain and Portugal, and Spanish is dominant (Portuguese in Brazil and French in Haiti), it is called Latin America.
Today, the Latin American market has become a new cross-border blue ocean recognized by the industry, attracting major e-commerce platforms and countless domestic brands to sail and set sail in Latin America. The rise of cross-border markets in Latin America has benefited from the following conditions:
First, the land is vast and the population is large
Latin America occupies a land area of 20.7 million square kilometers, accounting for nearly 13% of the earth's land surface area. The rich and changeable geographical and climatic environment has brought rich and diverse natural resources. Agriculture, forestry, fishing, minerals and other resources are very rich.
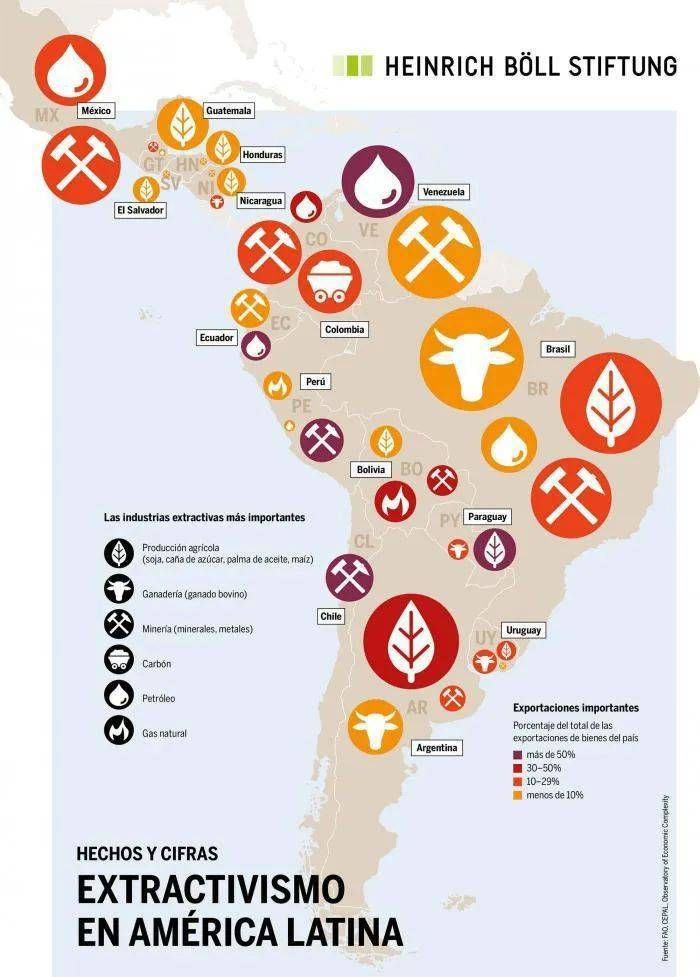
Map of natural resources in Latin America, source: google
Abundant natural resources have bred a large population. By 2021, the population of Latin America has exceeded 650 million. And the population growth is rapid, the growth rate is second only to Africa; The population tends to be younger, and the population under 65 accounts for more than 90%, making it one of the youngest regions in the world.
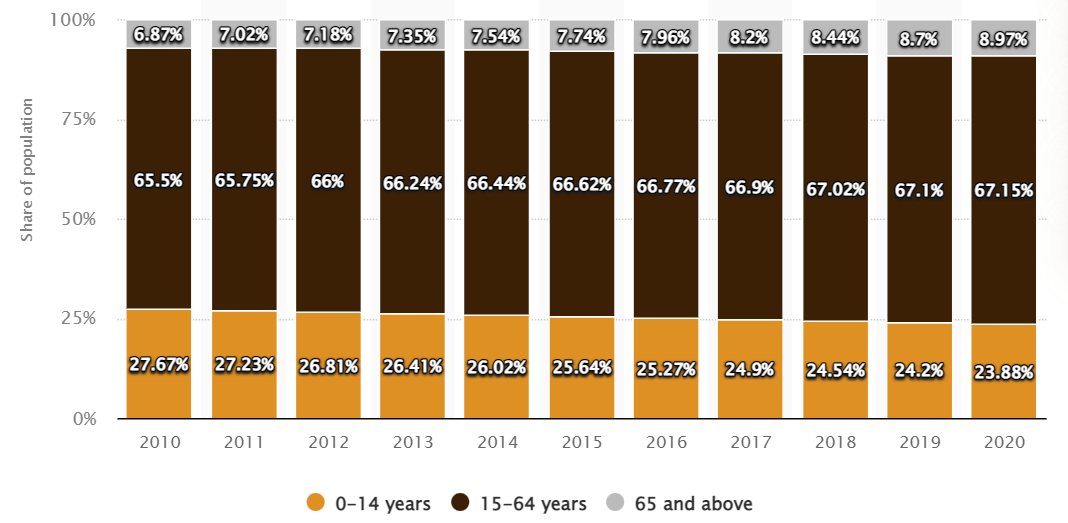
Latin American age composition map from 2010 to 2020, source: google.
II. Sustained economic growth and high degree of urbanization
Abundant natural resources and a rapidly growing and younger population have laid a material and demographic foundation for the sustained economic growth in Latin America.
During the 200 years from 1820 to 2020, influenced by the turbulent colonial history and the long-term intervention of the United States, the economy of Latin America has maintained a growth trend despite several twists and turns. In 2021, the total GDP of Latin America reached 5.49 trillion US dollars. Ranked fourth in the world economy.
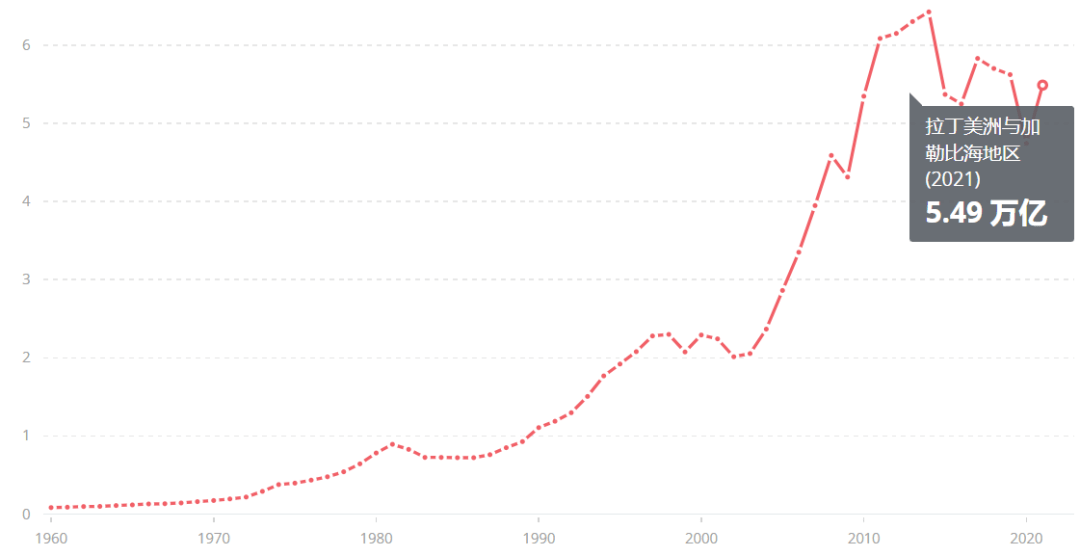
Source: World Bank
As early as 2018, of the 33 countries in Latin America, 20 were middle-income countries with a per capita GDP of less than $10,000, and 12 countries had a per capita GDP of more than $10,000. Some countries have stepped into the ranks of high-income and even developed countries: Uruguay's per capita GDP is $17,278, Chile's per capita GDP is $15,932, and Panama's per capita GDP is $15,575, all of which meet the standards of high-income countries; The per capita GDP of Costa Rica and Argentina is US$ 12,026 and US$ 11,678 respectively, which is close to the threshold of high-income countries. The per capita GDP of Brazil and Mexico, the two largest economies in Latin America, is US$ 8,921 and US$ 9,694 respectively, which is getting closer and closer to the goal of high-income countries.
At the same time, Latin America has always been the region with the largest growth rate and proportion of urban population among developing countries and regions. In 2013, the overall urbanized population reached more than 80%, and it is expected to reach 85% in 2025.
Third, the industrial development is unbalanced, and the online shopping crowd is on the rise
If the income and urban population in Latin America provide the consumption power of online shopping, then the unbalanced industrial development, the weakness of emerging manufacturing industries and the outbreak of COVID-19 epidemic have spawned the demand for cross-border online shopping.
Due to the failure to adjust import substitution industrialization to export orientation in time, Latin America lost its competitive advantage in global trade, and the proportion of manufacturing industry in the national economy dropped from 24.51% in 1989 to 12.92% in 2018. In contrast, it is the demand for e-commerce generated by the continuous improvement of network coverage. In 2021, the growth rate of online retail in Latin America reached 23.2%.

In 2021, the growth rate of e-commerce in Latin America ranked first in the world; Image source sees watermark
At the same time, cheap smart phones from China enable people with low economic level to join the online shopping army, which promotes the growth of "e-commerce" applications.
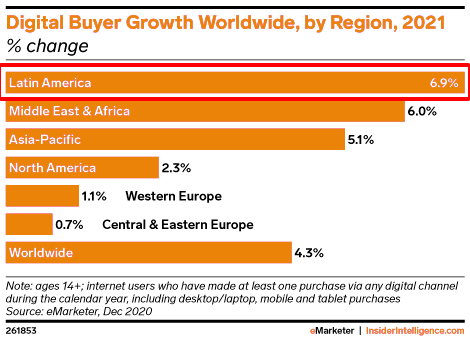
According to statistics, Latin America is the region that uses social networks the most in the world, with an average daily usage time of 212 minutes (the lowest in North America is 116 minutes). In 2021, the number of online shoppers in Latin America increased by 6.9%, higher than the global average of 4.3%.
It is estimated that by 2024, the number of online shoppers in Latin America will exceed 350 million.